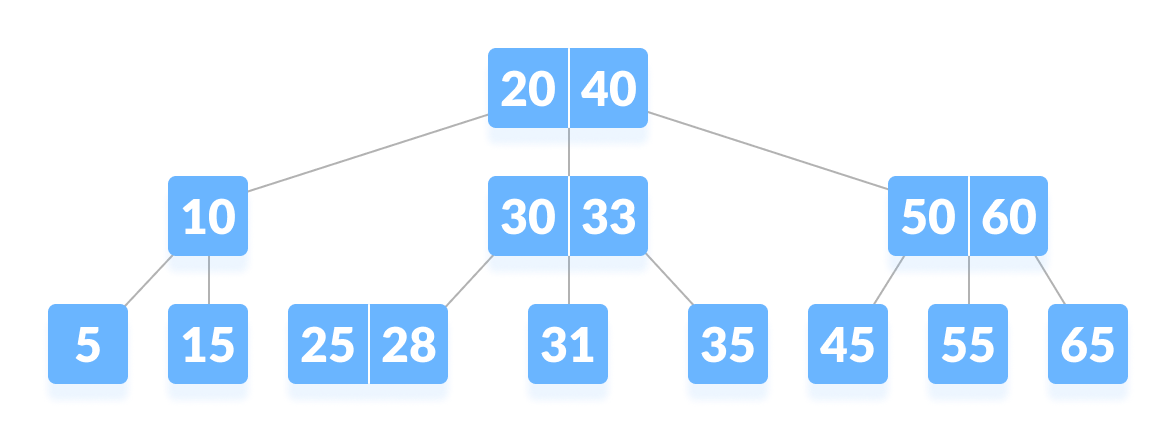
In computer science, a B-tree is a self-balancing Tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree generalizes the Binary search tree, allowing for nodes with more than two children. Unlike other Self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is well suited for storage systems that read and write relatively large blocks of data, such as databases and file systems.
((Programiz n.d.))
Each internal node of a B-tree contains a number of keys. The keys act as separation values which divide its subtrees. For example, if an internal node has 3 child nodes (or subtrees) then it must have 2 keys: \(a_1\) and \(a_2\) [(e.g. \(30\) and \(33\) in the image above)]. All values in the leftmost subtree will be less than \(a_1\), all values in the middle subtree will be between \(a_1\) and \(a_2\), and all values in the rightmost subtree will be greater than \(a_2\).
Properties
For a given B-tree of order \(m\):
- Each Vertex has at most \(m\) children
- The root has at least two children unless it’s a leaf
- Internal (non-leaf) Vertices store:
- Pointers to child Vertices
- Keys which indicate the bounds of the elements in the leaves below.
- Internal Vertices have between \(\lceil m/2 \rceil\) and \(m\) children
- Internal Vertices with \(k\) children have \(k - 1\) keys
- Leaf Vertices store data
- Leaf Vertices are all on the same level
Operations
Lookup
Lookup in a B-tree is straightforward. Given a node to start from, we use a simple linear or binary search to find whether the desired element is in the node, or if not, which child pointer to follow from the current node.
Time complexity
Worst case: \(\bigo{\log n}\)
Insertion
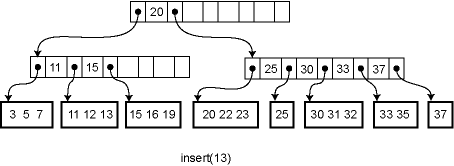
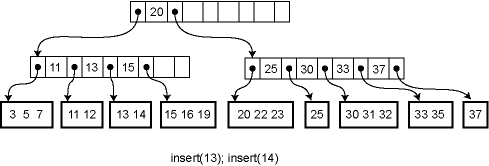
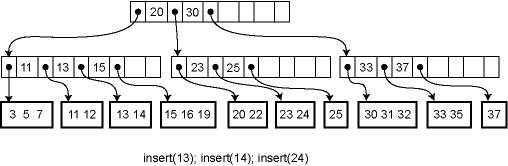
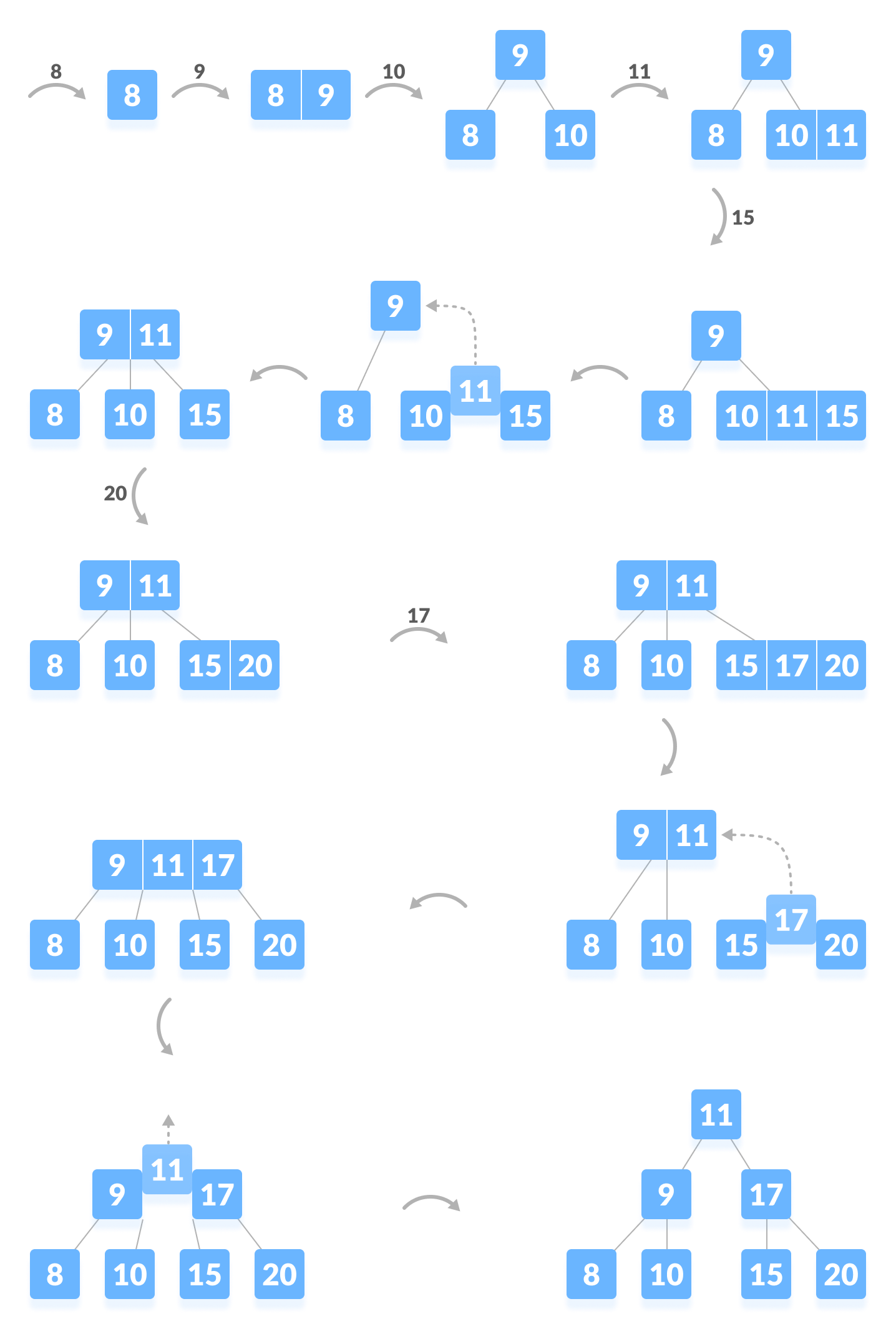
Insertion and deletion from a B-tree are more complicated; in fact, they are notoriously difficult to implement correctly. For insertion, we first find the appropriate leaf node into which the inserted element falls (assuming it is not already in the tree). If there is already room in the node, the new element can be inserted simply. Otherwise the current leaf is already full and must be split into two leaves, one of which acquires the new element. The parent is then updated to contain a new key and child pointer. If the parent is already full, the process ripples upwards, eventually possibly reaching the root. If the root is split into two, then a new root is created with just two children, increasing the height of the tree by one.
For example, here is the effect of a series of insertions. The first insertion (13) merely affects a leaf. The second insertion (14) overflows the leaf and adds a key to an internal node. The third insertion propagates all the way to the root.
((“B-Trees” n.d.))
((“Insertion into a B-tree” n.d.))
Time complexity
Worst case: \(\bigo{\log n}\)
Deletion
Deletion works in the opposite way: the element is removed from the leaf. If the leaf becomes empty, a key is removed from the parent node. If that breaks invariant 3, the keys of the parent node and its immediate right (or left) sibling are reapportioned among them so that invariant 3 is satisfied. If this is not possible, the parent node can be combined with that sibling, removing a key another level up in the tree and possible causing a ripple all the way to the root. If the root has just two children, and they are combined, then the root is deleted and the new combined node becomes the root of the tree, reducing the height of the tree by one.
Time complexity
Worst case: \(\bigo{\log n}\)