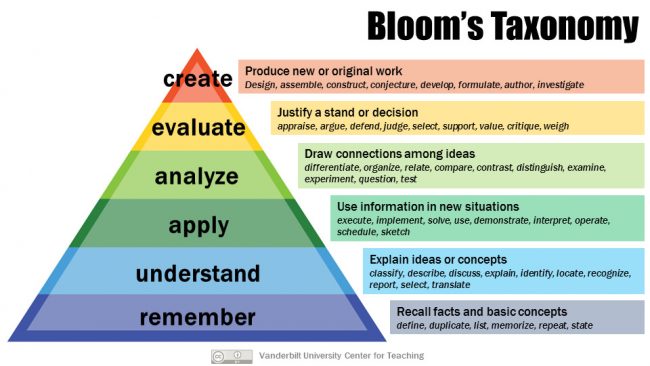
Bloom’s taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. […] The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives, assessments and activities.
The models were named after Benjamin Bloom [Benjamin Bloom], who chaired the committee of educators that devised the taxonomy.
In order from least complex to most complex:
- Knowledge
- Comprehension
- Application
- Analysis
- Synthesis
- Evaluation
Revised taxonomy
Bloom proposed a revision in 2001 (Anderson and Krathwohl 2001).
Remember (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
[…] involves recognizing or remembering facts, terms, basic concepts, or answers without necessarily understanding what they mean.
Spaced repetition systems are most effective here.
Example
Name three common varieties of apple.
Understand (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
[…] involves demonstrating an understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, summarizing, translating, generalizing, giving descriptions, and stating the main ideas.
Example
Summarize the identifying characteristics of a Golden Delicious apple and a Granny Smith apple.
Apply (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
[…] involves using acquired knowledge to solve problems in new situations. This involves applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules. Learners should be able to use prior knowledge to solve problems, identify connections and relationships and how they apply in new situations.
Example
Would apples prevent scurvy, a disease caused by a deficiency in vitamin C?
Analyze (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
Analysis involves examining and breaking information into component parts, determining how the parts relate to one another, identifying motives or causes, making inferences, and finding evidence to support generalizations.
Example
Compare and contrast four ways of serving foods made with apples and examine which ones have the highest health benefits.
Evaluate (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
Evaluation involves presenting and defending opinions by making judgments about information, the validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
Example
Which kinds of apples are suitable for baking a pie, and why?
Create (Bloom’s Taxonomy)
[…] involves building a structure or pattern from diverse elements; it also refers to the act of putting parts together to form a whole or bringing pieces of information together to form a new meaning.
This corresponds to Sensemaking (Klein and Baxter 2006).
Example
Convert an “unhealthy” recipe for apple pie to a “healthy” recipe by replacing your choice of ingredients. Argue for the health benefits of using the ingredients you chose versus the original ones.
Mnemonic
Red undies attract all evil cats