A binary heap is a Heap Data structure that takes the form of a Binary tree. Binary heaps are a common way of implementing Priority queues.
[…]
A binary heap is defined as a binary tree with two additional constraints:
- Shape property: a binary heap is a Complete binary tree; that is, all levels of the tree, except possibly the last one (deepest) are fully filled, and, if the last level of the tree is not complete, the nodes of that level are filled from left to right.
- Heap property: the key stored in each node is either greater than or equal to (≥; Max heap) or less than or equal to (≤; Min heap) the keys in the node’s children, according to some total order.
[…]
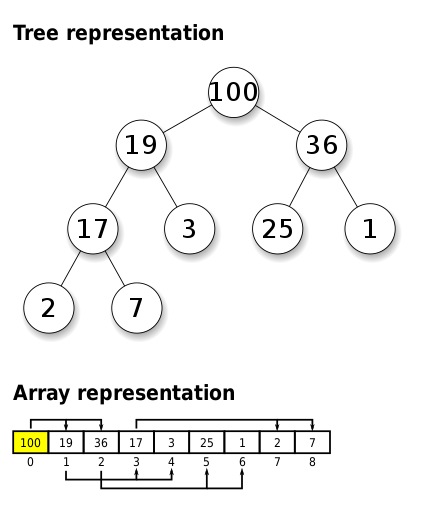
Binary heaps are also commonly employed in the heapsort sorting algorithm, which is an in-place algorithm because binary heaps can be implemented as an Implicit data structure, storing keys in an Array and using their relative positions within that array to represent child–parent relationships.
[formatting and links added]
Implementation
Operations
Insert
- Add the element to the bottom level of the heap at the leftmost open space.
- Compare the added element with its parent; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with its parent and return to the previous step.
Extract
- Replace the root of the heap with the last element on the last level.
- Compare the new root with its children; if they are in the correct order, stop.
- If not, swap the element with one of its children and return to the previous step. (Swap with its smaller child in a min-heap and its larger child in a max-heap.)
Bibliography
“Binary Heap.” 2022. Wikipedia, May. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Binary_heap&oldid=1087856345.