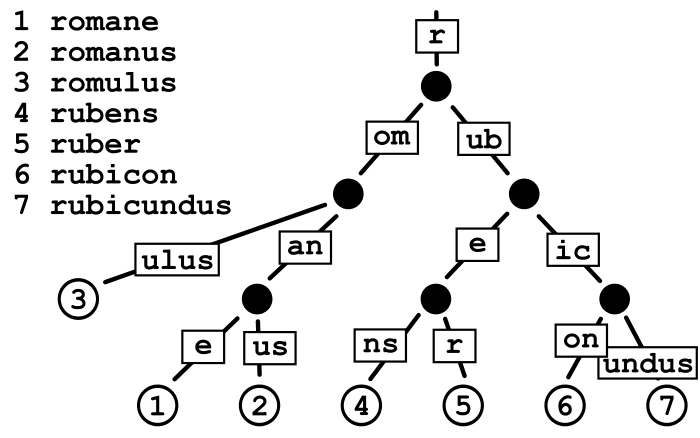
In computer science, a radix tree (also radix trie or compact prefix tree or compressed trie) is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie (Prefix tree) in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix \(r\) of the radix tree, where \(r\) is a positive integer and a power \(x\) of 2, having \(x \geq 1\). Unlike regular trees, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets (especially if the strings are long) and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.
Bibliography
“Radix Tree.” 2022. Wikipedia, August. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Radix_tree&oldid=1105756012.